Intel Launches Raptor Lake Refresh 14th Generation CPUs in Market : Features and Prices
On the cusp of the launch of the desktop CPU Arrow Lake-S from Intel, Intel has quietly launched a new CPU Raptor Lake Refresh of the 14th generation known as the “14001” series with only P nuclei. These CPUs are equipped with full cores and point to integrated solutions, but in a strange twist, the flagship model can be overclocked.
That’s the bad news: these chips only come in an integrated format, which hinders enthusiasts and conventional customers from accessing these CPUs that are not orthodox. The integrated form factors are a computer solution in which the CPU is installed in a machine from an OEM in the factory. So generally, these chips are sold with the plate base and cannot be replaced or updated easily.

The new line E-coreless Raptor Lake Refresh from Intel includes three SKUs Core i9, two variants of Core i7 and four models Core i5. In contrast, the most exclusive variant of the new models is the model insignia Core i9-14901KE, which, if we cannot tell by the model number, seems to be a piece of the K series with the ability to overclock. If this is true, the 14901KE is one of the only, if not the only, processor with integrated overclocking capability that Intel has created to date.
The new line from Intel is also very less orthodox, as it is the only line to date since the 12th generation that does not have any electronic core. However, there are some positive aspects in an alignment of this type. On the part of Intel, having E-coreless chips allows recycling Raptor Lake defective matrices that may have defective E cores but that function perfectly. Let’s suspect that this is the only reason why Intel decided to create this new line in the first place: to get rid of defective matrices that have probably been accumulating since the launch of the 14th generation.
Intel’s new line is also beneficial for consumers. One of the main disadvantages of Intel’s modern hybrid architectures is the added complexity of programming the work in cluster centers suitable for an optimal performance and an energy efficiency. Sometimes, the operating system programmers place some workloads on the incorrect cores, causing performance problems for the end user. Additionally, many workloads do not benefit from having E-cores; In turn, the only benefit is from having six or eight physical nuclei (or less).
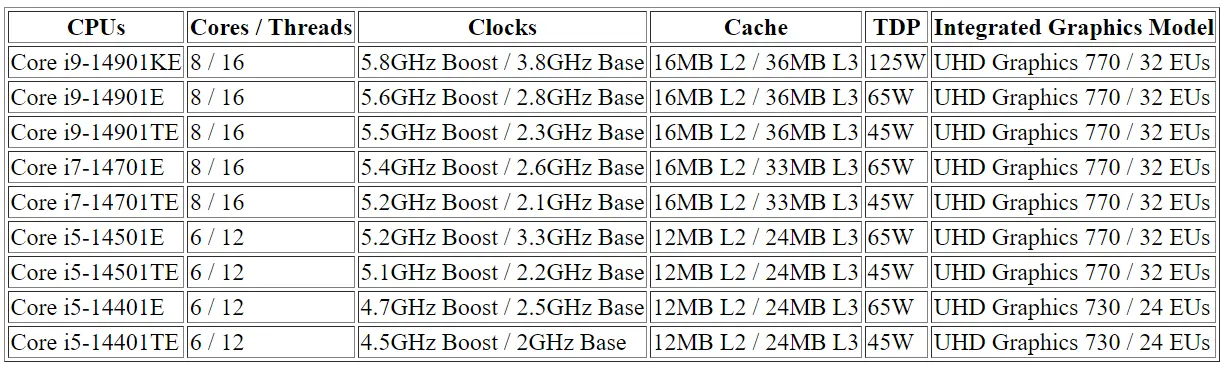
The last three variants of Core i9 have eight Raptor Cove cores, 16 subprocesses and 36 MB of L3 cache. The main differences between the three are clock speed and PBP/TDP. The model Insignia i9-14901KE has a TDP of 125 W, a clock turbo boost maximum of 5,8 GHz and a clock base of 3,8 GHz. The Core i9-14901E has a TDP of 65 W, although not significant, but only loses 200 MHz of its maximum clock speed, with a maximum turbo boost of 5,6 GHz. However, the clock base suffers a significant impact at 2,8 GHz. The i9-14901TE is the variant with greater power limitation and accounts with a PBP/TDP of 45 W. The maximum speed of the clock turbo is of 5,5 GHz and the clock base is of 2,3 GHz.
There is very little difference between the models Core i9 from the variants Core i7. Both Core i7 models also have eight cores and 16 subprocesses, but have slightly lower clock speeds and an extremely slight reduction in L3 cache. El Core i7-14701E has a TDP of 65 W, a turbo frequency of 5,4 GHz, a base frequency of 2,6 GHz and 33 MB of cache L3. El Core i7-14701TE has the same configuration of core and cache, but counts with a PBP/TDP of 45 W, a turbo maximum clock of 5,2 GHz and a base clock of 2,1 GHz.
The Core i5 receives a much bigger hit in the specifications sheet, with six cores, 12 subprocesses and 24 MB of L3 cache. The Core i5 line is divided into two sublines, the series 14501 and 14401, very similar to the desktop chips Core i5 14500 and i5 14400. Two main areas differentiating the sublines Core i5: the Core i5 14501 series comes with recharging frequencies. The range of 5 GHz, while the series 14501 comes with turbo maximum frequencies in the range of 4 GHz. The 14501 series is also the only group of chips of the E-coreless line of 14th generation Intel that uses low-range UHD 730 graphics with 24 UE. The rest of the i5, i7 and i9 use graphics UHD 770 with 32 EU.
